What is Telephone Cable and How Does it Work in Modern Communication
The evolution of modern communication has been profoundly influenced by the technology behind telephone cables. These essential components facilitate the transmission of voice and data across vast distances, forming the backbone of telecommunication systems worldwide. According to industry reports, the global telecommunications market is projected to reach approximately $1.7 trillion by 2025, with a significant share attributed to the infrastructure supported by telephone cables.
Telephone cables, composed of copper or fiber-optic materials, have undergone considerable advancements, enhancing their capacity and performance. Research indicates that fiber-optic cables can transmit data at speeds exceeding 1 Gbps, revolutionizing internet connectivity and voice communication. The importance of reliable telephone cable systems cannot be overstated, as they play a crucial role in maintaining seamless communication networks, particularly in an era where digital interaction is paramount.
As we delve deeper into the mechanics of telephone cables, it becomes evident that these seemingly simple wires are intricate systems that enable the flow of information efficiently and effectively. Understanding the workings of telephone cables not only highlights their significance in today’s telecommunication landscape but also sheds light on the future advancements that promise to further connect our global community.

Overview of Telephone Cable Types and Specifications
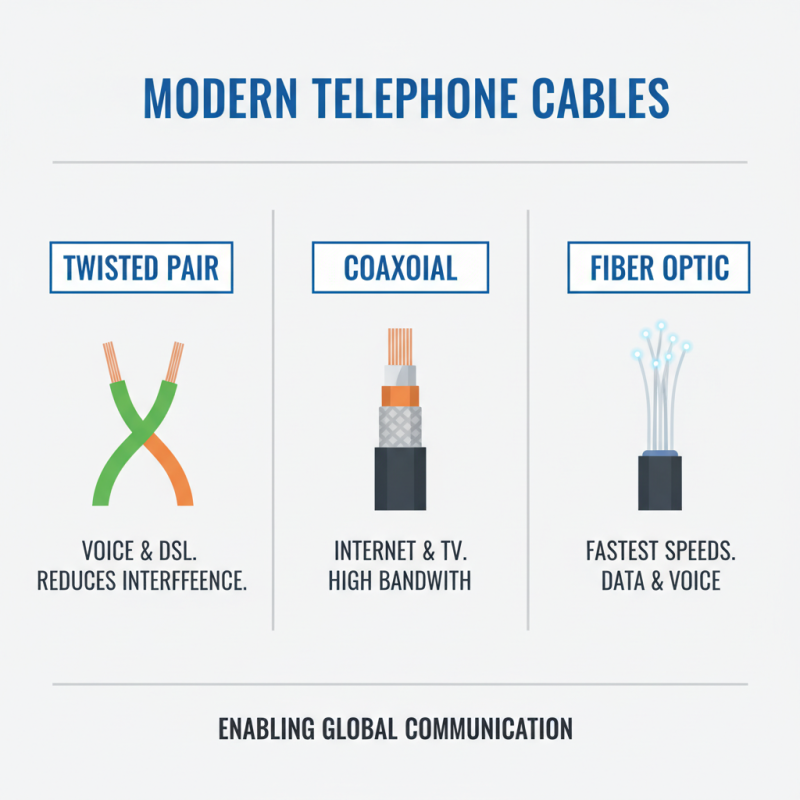
Telephone cables play a crucial role in modern communication by enabling voice transmission over long distances. There are several types of telephone cables, each tailored for specific applications and environments. The most common types include twisted pair cables, coaxial cables, and fiber optic cables. Twisted pair cables, which are predominantly used for standard telephone lines, consist of pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together. This design helps reduce electromagnetic interference, making it ideal for voice communication.
Coaxial cables, although more commonly associated with television and internet services, also have applications in telephone systems. They feature a central conductor surrounded by insulating material and an outer conductive layer, providing enhanced protection against interference. Fiber optic cables, on the other hand, are becoming increasingly popular in telecommunication due to their ability to transmit data at high speeds over long distances with minimal loss. They use light signals for communication, making them immune to electromagnetic interference, and are capable of supporting a greater bandwidth than traditional copper cables.
When considering telephone cable specifications, key factors include the gauge of the wire, the number of pairs in a cable, and the material used. These specifications determine the cable's performance, including its ability to support various data rates and communication distances. Understanding these types and specifications is essential for ensuring optimal performance and reliability in modern communication systems.
How Telephone Cables Facilitate Voice and Data Transmission
Telephone cables play a crucial role in modern communication, enabling the transmission of voice and data over long distances. These cables, typically made up of multiple insulated copper or fiber optic wires, are designed to carry electrical signals that represent sound. In traditional telephone systems, the analog voice signals are converted into electrical signals that travel through the copper wires, while in modern systems, fiber optic cables transmit data in the form of light signals, providing faster and more reliable communication.
The structure of telephone cables enhances their ability to facilitate this transmission. Each wire within the cable can carry a different channel, allowing multiple conversations to occur simultaneously without interference. Additionally, advancements in technology, such as digital signal processing, have improved the efficiency and clarity of the transmitted signals. This process minimizes noise and distortion, ensuring that voice calls and data transfers are delivered with high fidelity. Overall, telephone cables are a backbone of our communication infrastructure, enabling both personal and professional exchanges in today’s digital age.
What is Telephone Cable and How Does it Work in Modern Communication
| Dimension | Details |
|---|---|
| Type of Cable | Twisted Pair, Coaxial, Fiber Optic |
| Primary Use | Voice Transmission and Data Communication |
| Data Rate | Up to 1 Gbps (Gigabits per second) with modern standards |
| Transmission Distance | Typically up to 100 meters for twisted pair cables |
| Frequency Range | From 1 kHz to several GHz depending on cable type |
| Signal Loss | Varies by cable type; generally lower in fiber optics |
| Installation Environment | Indoor and Outdoor options available |
| Legacy Systems | POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service), DSL |
The Role of Insulation and Shielding in Telephone Cables
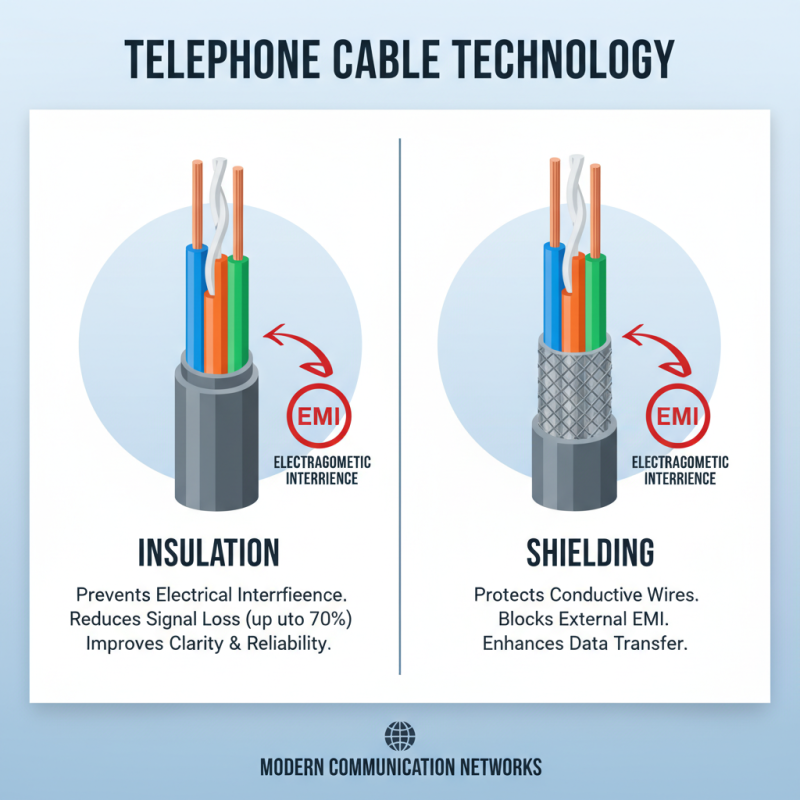
Insulation and shielding play a crucial role in the functionality and performance of telephone cables used in modern communication. Insulation is primarily responsible for preventing electrical interference and protecting the conductive wires inside the cable. Typically made from materials such as polyethylene or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), insulation minimizes signal loss due to external electromagnetic interference (EMI), which can arise from nearby electrical lines or devices. According to a report by the Telecommunications Industry Association, effective insulation can reduce signal degradation by up to 70%, significantly enhancing the clarity and reliability of voice and data transfers.
Shielding, on the other hand, complements insulation by providing an additional barrier against interference. It typically consists of a layer of conductive material, such as copper or aluminum foil, that surrounds the insulated conductors. This feature not only protects the signal from external noise but also reduces crosstalk between pairs of wires within the cable. The International Electrotechnical Commission highlights that properly shielded telephone cables can improve overall signal integrity, with some high-performance cables achieving a reduction in noise levels by as much as 30 dB. Such advancements in insulation and shielding technologies are essential for maintaining high-quality communication services in an increasingly data-driven world.
Modern Advances in Telephone Cable Technology
Modern telephone cable technology has seen significant advancements, primarily driven by the increasing demand for high-speed communication and the proliferation of digital services. These cables are now designed not just for transmitting voice signals but also for carrying data and multimedia content. The use of twisted pair cables, fiber optics, and enhanced materials have allowed for greater bandwidth and reduced interference. This shift enables clearer calls and faster internet speeds, reflecting the needs of contemporary communication systems.
Additionally, innovations such as improved insulation and shielding techniques have made telephone cables more resilient to environmental factors and electromagnetic interference. These enhancements ensure consistent performance and reliability, critical for both residential and commercial applications. Furthermore, the integration of digital signal processing technology within telephone cables has facilitated more efficient data transmission, paving the way for advanced services such as VoIP and high-definition video calling. As technology continues to progress, telephone cables will remain at the forefront of connecting people worldwide, adapting to ever-evolving communication needs.
Advances in Telephone Cable Technology
Impact of Telephone Cables on Global Communication Systems
Telephone cables have been a fundamental part of global communication systems since their inception, serving as the backbone for voice and data transmission. These cables connect households and businesses to telecommunication networks, facilitating everything from simple voice calls to complex data exchanges. By enabling reliable communication over vast distances, telephone cables have significantly contributed to the interconnectivity of the modern world, allowing economies and cultures to interact seamlessly.
One key aspect of telephone cables' impact on global communication is their role in rural and underserved areas. Many regions rely on traditional copper telephone lines for connectivity, which have been crucial for bridging the digital divide. As countries work to improve their infrastructure, the advancement from copper to optical fiber cables allows for higher bandwidth and faster data transfer rates, enhancing communication capabilities and stimulating economic growth.
Tips: When considering the installation of telephone cables, evaluate the specific needs of your communication requirements. Opt for fiber optic cables if you prioritize speed and bandwidth, while traditional copper may still be sufficient for basic voice services. Regular maintenance is also essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the cables in your communication network.
Related Posts
-

2025 Top 5 Telephone Cables: Enhance Your Connectivity Experience Today
-

2025 Top 10 Network Cables: Best Options for Speed and Reliability
-

The Ultimate Guide to Understanding Wire Cable Types for Your Projects
-

Exploring the Science Behind RCA Cables: How They Connect Your Audio and Video Devices
-
Harnessing Fiber Optic Adapter Innovations at China Import and Export Fair 2025
-

How to Choose the Right Wire Cable for Your Electrical Project
