Top Benefits of Fiber Optic Cable for High Speed Internet Connectivity?
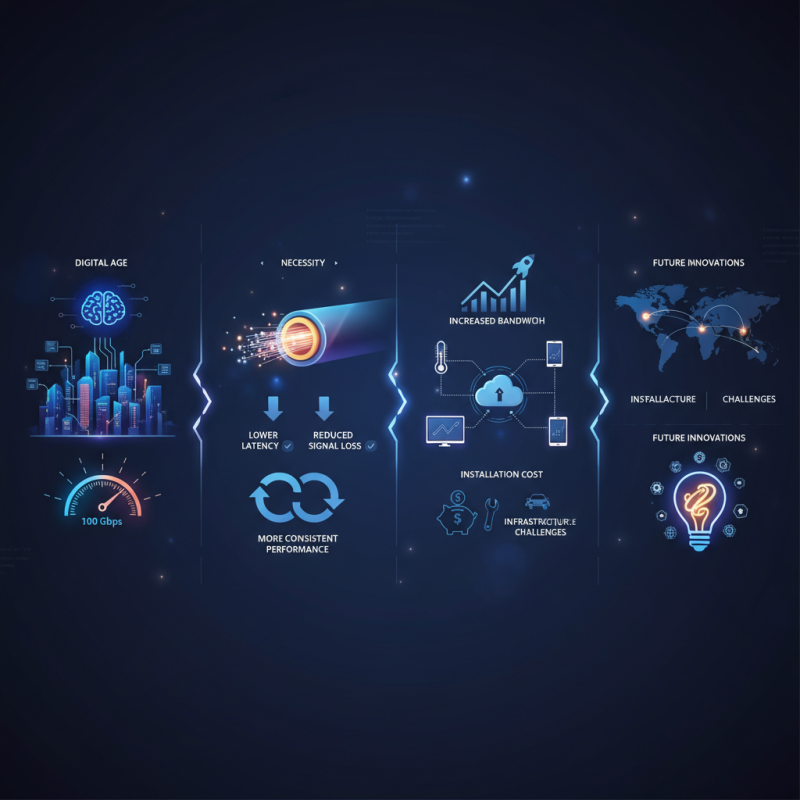
In today's digital age, high-speed internet is a necessity. The demand for faster, more reliable connections continues to grow. According to a report by the Fiber Optic Association, fiber optic cable can transmit data at speeds up to 100 Gbps. This is critical for both businesses and individuals who rely on quick access to information.
Fiber optic technology uses light signals, which offer significant advantages over traditional copper cables. With lower latency and reduced signal loss, users experience more consistent performance. However, many still opt for older technologies without understanding the risks tied to slower connections. Additionally, as we move into a more connected world, the need for bandwidth increases. The expansion of smart devices and IoT applications requires infrastructure that can keep up.
Despite the evident benefits, transitioning to fiber optic systems has challenges. Installation may be cost-prohibitive for some, and the infrastructure is not yet ubiquitous. This raises questions about accessibility and potential disparities in internet quality. As we navigate these issues, recognizing the transformative potential of fiber optic cable remains vital for future innovations.

Key Features of Fiber Optic Cable in Internet Connectivity
Fiber optic cable has emerged as a game changer in internet connectivity. One key feature is its ability to transmit data over long distances with minimal loss. This translates to faster internet speeds and more reliable connections. According to reports, fiber optic connections can reach speeds of up to 1 Gbps or more. This far exceeds traditional copper cables, which struggle to keep pace with rising demands.
Another significant benefit is that fiber optics are less susceptible to interference. Unlike copper cables, they do not carry electrical currents. This makes them ideal for urban areas with high electromagnetic noise. However, it’s important to note that installation can be challenging. The fragility of fiber optic cables requires skilled technicians for proper setup. Improper handling can lead to significant performance issues.
Moreover, fiber optic technology facilitates better bandwidth capabilities. This is crucial for streaming, gaming, and professional applications. With the demand for high-speed internet steadily increasing, outdated infrastructure can become a bottleneck. Despite its advantages, some households may still rely on slower connections. This is a gap that needs addressing to ensure equitable access to high-speed internet.
Advantages of Fiber Optic Cable Over Traditional Copper Wiring
When comparing fiber optic cables to traditional copper wiring, the differences are striking. Fiber optic technology uses light to transmit data, while copper relies on electrical signals. Consequently, fiber optic cables can support much higher bandwidths. According to a report from the Fiber Broadband Association, fiber networks can offer speeds exceeding 1 Gbps, while copper typically caps at around 100 Mbps.
One major advantage is the distance. Fiber optic cables maintain consistent performance over long distances. For example, signals can travel up to 40 kilometers without signal loss, whereas copper can only manage about 100 meters before degrading. This makes fiber ideal for expansive networks, such as those in urban areas.
Tip: Consider the future scalability of your internet needs. Fiber optic is not just faster; it's more adaptable. When planning network upgrades, fiber should be top of the list.
Environmental factors impact wiring performance too. Copper is susceptible to electromagnetic interference, which can disrupt services. In contrast, fiber optic cables are immune to this type of interference. They also have a higher resistance to temperature fluctuations and moisture, assuring reliability in various conditions.
Tip: Ensure proper installation to fully utilize fiber’s benefits. Even the best cables underperform without skilled installation. Understanding these elements can lead to informed decisions for long-term connectivity solutions.
Impact of Fiber Optic Technology on Internet Speed and Bandwidth
Fiber optic technology has transformed internet speed and bandwidth dramatically. Unlike traditional copper cables, fiber optics transmit data as light signals. This method allows for faster data transfer rates, reaching up to gigabit speeds. The enhanced speed means users experience smoother video streaming, quicker downloads, and seamless online gaming. On the contrary, many still rely on older technologies that can't match these speeds, creating a frustrating digital divide.
The impact on bandwidth is equally significant. Fiber optic cables offer greater capacity for data transmission compared to their copper counterparts. This increased bandwidth supports more users and devices simultaneously without slowing down internet service. However, not all areas have access to fiber optics yet. Some communities lag behind, still grappling with limited connectivity options. This gap underscores the importance of expanding fiber infrastructure to bridge the divide.
Transitioning to fiber optics isn't without challenges. Installation can be costly and time-consuming. Additionally, some users may find it difficult to adapt to new technology. Yet, embracing fiber optics is essential for future-proofing internet connectivity. As demand for faster, more reliable internet grows, fiber optics is poised to meet those needs effectively.
Impact of Fiber Optic Technology on Internet Speed and Bandwidth
Long-distance Connectivity Solutions with Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables offer exceptional benefits for long-distance connectivity. They transmit data over vast distances without significant loss. Unlike traditional copper cables, fiber optics can carry more data at higher speeds. This makes them ideal for regions that require reliable internet access.
One of the core advantages is reduced latency. Fiber optic cables facilitate seamless communication and faster data transfer. This is crucial for businesses relying on real-time data. However, installing fiber optic networks can be expensive and time-consuming. The costs may lead some organizations to hesitate.
While fiber optics dominate long-distance internet solutions, their installation adds challenges. The infrastructure might not be in place everywhere. Moreover, some locations face regulatory hurdles that delay deployment. These issues require careful planning and consideration for successful implementation. Overall, fiber optics provide significant benefits, but embracing them means facing some realities.
Top Benefits of Fiber Optic Cable for High Speed Internet Connectivity
| Benefit | Description | Impact on Connectivity |
|---|---|---|
| High Speed | Fiber optic cables provide extremely high data transfer speeds, often exceeding 1 Gbps. | Enhances user experience for streaming, gaming, and remote work. |
| Long Distance Transmission | Optical signals can travel over long distances without significant loss. | Ideal for connecting remote locations without repeaters. |
| Increased Bandwidth | Fiber optics can carry more data at once compared to copper cables. | Supports multiple users and high-demand applications simultaneously. |
| Low Interference | Less susceptible to electromagnetic interference than copper cables. | Ensures consistent quality and signal integrity. |
| Future-Proof Technology | As technology advances, fiber optics can accommodate higher data rates easily. | Reduces the need for frequent upgrades or replacements. |
| Enhanced Security | Difficult to tap into without detection compared to electrical signals. | Provides a more secure connection for sensitive data transmission. |
Future Trends in Fiber Optic Internet Infrastructure Development

The future of fiber optic internet infrastructure development looks promising but also challenging. As more cities prioritize high-speed connectivity, the demand for fiber optics grows. However, installation can be complex. Urban areas face obstacles with existing infrastructure, making it hard to integrate new lines seamlessly. Planners must navigate through buildings and municipal regulations.
Emerging technologies play a critical role in shaping fiber optic networks. For instance, advancements in automation can streamline deployment. Yet, these innovations require investment and training. Smaller service providers might struggle to keep pace with these changes, creating disparities in access. Sustainable practices in installation are also increasingly important. Environmental concerns cannot be overlooked. With the push towards greener technologies, fiber optic solutions must adapt. Balancing speed, cost, and ecological impact remains a tightrope walk for developers.
Related Posts
-

Why You Should Choose Fiber Optic Patch Cable for Reliable High Speed Internet Connection
-
Emerging Trends in HDMI Fiber Optic Cable Market at 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-

2025 Top Fiber Optic Patch Cables: High-Speed Solutions for Modern Connectivity
-

2025 Top 5 Fiber Network Cable Innovations for High Speed Connectivity
-

How to Choose the Right BNC Adapter for Your Needs: A Complete Guide
-

Exploring HDMI Switcher Innovations at the 138th Canton Fair in 2025
